International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-2013 1065
ISSN 2229-5518
Shilpi Chauhan1, Ravi Prakash2, DBV Singh1,
—————————— ——————————
Langmuir probe is a diagnostic tool, a metallic probe to
diagnose the Plasma. The probe gives the characteristics of the plasma in absence of external interference It is used for measuring electron temperature, electron density, floating potential, ion saturation current. By varying the bias voltage of the probe, the current–voltage characteristics were measured and electron temperature, electron density and electron saturation current were calculated. These measurements are important to study plasma characteristics. Maxwell- Boltzmann distribution is a theoretical calculation limit which is achieved if the whole plasma and its surroundings are in complete thermodynamic equilibrium. Hence some deviation from the theoretical curve is expected in experiment.
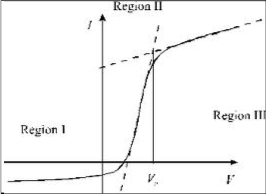
The current voltage characteristics are mainly divided in three regions:
Langmuir probe positive ions are collected on the tip of
Langmuir probe which gives a change in voltage across the
Region 2: In this region bias voltage is kept positive and is varied up to plasma potential. This region is called as the Electron retardation region, with linear line between the bias voltage and probe current. Flow of positive ions and electrons are equal results in net zero current.
Region 3: In this region, bias voltage is greater than the plasma potential (V>Vs ). The electrons get accelerated due to the positive bias voltage.
————————————————
• Shilpi Chauhan is currently pursuing masters degree program in
Measurement and Control in ITM University, Gwalior, Mob. 7405145162
E-mail: shilpi.chauhan06@gmail
• Mr. N. Ravi Prakash is currently in Institute for Plasma Research, Gandhinagar, Gujaray, E-mail: prakashipr@gmail.com
• Mr. DBV Singh is Asst. Prof. in ITM University, Gwalior, E- mail: dbvsingh@gmail.com
resistor is known as ion saturation current (Isi )
IJSER © 2013 http://www.ijser.org
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-2013 1066
ISSN 2229-5518
DC Power Supply, Nitrogen gas, Vacuum.
Probe current, current-Voltage characteristics, Electron temperature, electron density, electron Saturation current and floating potential.
Langmuir Robe works by inserting one or more electrode into the plasma and observing the current to the probe as a function of difference between the probe and the plasma space potential can determine the basic Plasma parameters.
There are three methods of Plasma diagnostics and plasma parameter measurement using Langmuir probes namely
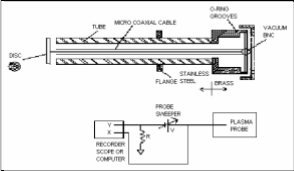
Single Langmuir probe consist of one electrode which is inserted in the Plasma and used to measure current through the probe as a function of the difference of the potential. These values are current can be use full to diagnose the other basic parameters of Plasma like floating potential, electron temperature, electron density and electron saturation current.
Fig2. Single Langmuir Probe with electronic circuit [6]
It has two electrodes with same diameter and equal surface area with a small gap between these electrodes. Double Langmuir Probe with an electronic circuit for giving the bias voltage is developed for determining the current-voltage characteristics and from these characteristics other parameters has to calculate. Constructional view and experimental results are given in this paper. Langmuir Probe with electronic circuit is given in fig: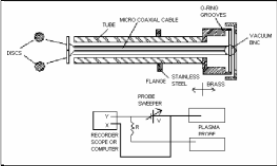
Fig3. Double Langmuir Probe with electronic circuit [6]
In this experiment, Double Langmuir Probe was made of tungsten electrode with pointed tip collecting the positive ions or electrons depending on the condition applied.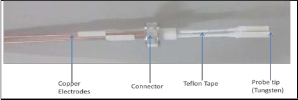
Fig2. Constructional view of probe
Triple Langmuir probe consist of three electrodes with same surface area and same gap between electrodes. It is designed to measure very accurate current voltage characteristics and using these curves, other parameters can also calculate. Triple Langmuir probe is very complicated because of its construction and measurements are not easy to calculate.
IJSER © 2013 http://www.ijser.org
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-2013 1067
ISSN 2229-5518
Block diagram for setup:
exploiting the linearity of the second region temperature can be realized as the reciprocal of the slop of the measured line in this region and also from the Plasma potential and floating potential.
Plasma electron temperature is calculated in second region of
the current-voltage characteristics (Fig 1) Expression used for temperature calculation is:![]()
2𝑀
𝑇𝑒 = 2(𝑉𝑠 − 𝑉𝑓)𝑒/𝑘 ∗ ln �𝜋𝑚�
found at the time when we applied bias voltage much greater than the Plasma potential. In this case almost all the velocity will reach the collector and from here current – voltage characteristics has to be plotted.
It is given by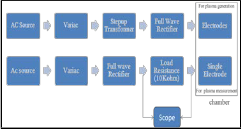
Experimental setup:
ln[I probe – I sat ] =![]()
𝑄
𝑘𝑇𝑒
(Vbias - Vf)
Electron Density: Electron density is depending upon the electron temperature. A assignment of non-Maxwellian electron energy distribution is difficult. One more useful parameter in this paper is the mean electron energy Ce . The mean energy is known to be proportional to the second derivative of the electron current with respect to the voltage. By finding the mean electron energy, the electron density can be found from given expression
4 ∗ 𝐼𝑠𝑎𝑡
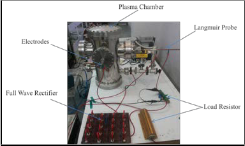
Fig3. Setup for Probe measurement
Full wave rectifier is used to convert AC power in DC source. DC power supply is given to electrodes placed inside the chamber to generate the plasma between two electrode plates. Plasma current and voltage is measured across the resistor that is connected with Langmuir Probe. Current is measured across the resistance of 10kohm connected in between bias voltage and two Langmuir probe. Measured
current is known as probe current.
𝑛𝑒 =![]()
𝑒 ∗ 𝐴𝑝 ∗ 𝐶𝑒
Setup for measurement:
The mean energy for a Maxwellian distribution is given,![]()
8𝑘𝑇𝑒
Where-![]()
𝐶𝑒 = �
𝜋𝑚
Te = Electron temperature
Vs = Plasma voltage
Vf = Floating potential
M = Ion mass
e = Electron charge m = Electron mass
k = Boltzmann constant
ne = electron density
Fig4. Plasma generation Setup
IJSER © 2013 http://www.ijser.org
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-2013 1068
ISSN 2229-5518
Measured current voltage characteristic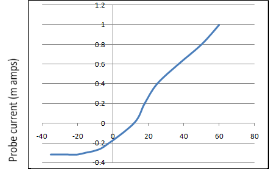
![]()
Fig5. Current-voltage characteristics of the plasma
The current-voltage characteristic of the plasma which formed using nitrogen gas.
Calculated parameters are-
Parameters | Calculated Values |
Floating Potential | 12volt |
Electron Temperature | 19.96*104 Kelvin |
Electron Density | 3.93*1013 m-3 |
Electron Saturation current | 0.2467 m amp |
Debye Length | 1.856 mm |
In this paper, Langmuir Probe sensor has been described and developed. The main plasma parameters that can be reliably extracted from current-voltage response are electron temperature, electron density, electron saturation current and plasma potential. Variation of these parameters is obtained by varying the position of probe in plasma chamber.
The work was carried out M. Tech at Institute for Plasma
Research under guidance of Mr. Ravi Prakash. I am very thankful to Institute for Plasma Research for giving me opportunity for doing this project.
[1] David Sirajuddin, Nuclear Engineering & Radiological Sciences “Determination of Plasma Parameters of an Argon RF Plasma Using a Langmuir Probe” April 6, 2007.
[2] Robert L. Merlino Department of Physics and Astronomy The University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa 52242 “Understanding Langmuir probe current-voltage characteristics” Received 26
February 2007; accepted 14 July 2007
[3] Luis Conde Departamento de Física Aplicada E.T.S. Ingenieros Aeronáuticos Universidad Politécnica de Madrid
28040 Madrid, Spain. “An introduction to Langmuir probe to
diagnostics of plasmas” May 28, 2011
[4] M. Y. Naz and A. Gha®ar Department of Physics University of Agriculture Faisalabad, Pakistan, N. U. Rehman Department of Physics COMSTS Institute of Information Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan, S. Naseer Departments of Physics University of Peshawar, Peshawar 25120, Pakistan, M. Zakaullah Departments of Physics, Quaid-I-Azam University, Islamabad 45320, Pakistan “DOUBLE AND TRIPLE LANGMUIR PROBES MEASUREMENTS IN INDUCTIVELY COUPLED NITROGEN PLASMA” Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 114, 113{128, 2011
[5] Edbertho Leal-Quirós, Ph.D. Professor and Scientific Research Director Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico “ BASIC PLASMA DIAGNOSTICS PROBES”
[6] JournalNewMexicoPresentations.pdf
[7] Manash kumar Paul, Dhiraj Bora “ Langmuir probe Study in the nonresonant current driveregime of helicon discharge” PRAMANA journal of physics vol. 71, No. 1, July 2008
[8] Mavardi_langmuir Probe_AJP_1966.pdf
[9]Primer on “Gas Discharges” (Plasmas)/plasma discharge.pdf
[10] Yan Zong – cheng, Chen Li, Wang Hong-lin “Experimental study of Plasma Under- liquid electrolysis in hydrogen generation” Chines journal of process engineering, vol. 6 No. 3, June 2006.
IJSER © 2013 http://www.ijser.org
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-2013
ISSN 2229-5518
1069