International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-2013 1154
ISSN 2229-5518
Decrypted Stegnography
Ankit Shah Ninad Mehendale Dwarkadas.J.Sanghvi College of Engineering Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Electronics and Telecommunication Department Department of Bio-Sciences and Bio-Engineering
Abstract— We have designed an image processing technique called as Decrypted Stegnography by using simple programming methods. We can send confidential data which will be hidden behind a formerly shuffled image. The data remains so secure that while it is being sent to some other place no one is able to retrieve it. This happens as the image that is being sent is without any appreciable change in its appearance and thus the hacker wont be able to make out that in reality some data is being transmitted via the image. The data is finally received at the receiver end where it is decoded. The basic aim of the system is thus to transmit important data from one place to another.It can be used in the fields of military and defense.
Index Terms— Encryption, Decryption, Confidential, Data, Image, Pixel and Bits..
—————————— ——————————
1 INTRODUCTION
ecrypted stegnograhy is a special type of data hiding technique by making use of images .It is an image
processing technique. It can be used to transfer extremely sensitive and confidential information. It can be widely used
by military and defense systems. First the image is encrypted
via a secret key. Now the information to be transferred is
stored in the LSB bit of the image pixel. Finally the image is
decrypted without any notable change in the appearance of
the image. This image can now be safely transferred. Even
if some hacker gets this image, he wont be able to get the data. At the receiver end the stored information can be recovered back by using the key for the encrypted image. Thus any sort of secretive information can be convened without any interfer- ence.
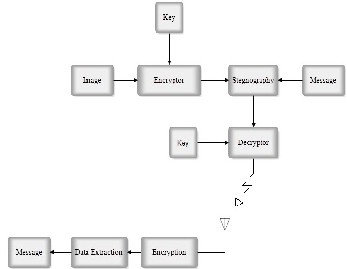
2 BLOCK DIAGRAM
3 WORKING
The process of changing the LSB of an image with any other data without changing the appearance of the image is called as image stegnography. Stegnography( from the Greek word for covered writing) refers to a method of hiding data , not just concealing its contents but concealing its very existence.[1] With modern day Stegnography , a message is embedded in seemingly innocuous cover data (e.g., a picture, text, or sym- bols) to hide the act of communication. [2]. It is used to trans- fer all types of confidential information. In the proposed sys- tem we first take any image. Then the process called encryp- tion is carried on image. In encryption, we interchange some
of the blocks of the image (Block cipher), which changes the
appearance of the actual image completely. After encryption
one can see that the image has been converted into Raster pat-
tern. The moving of the blocks in encryption is dependent on a specific key. Block shifting follows the key for blocks size and amount of shift. An image is made up of pixels. Each pixel is
of the size of 8 bit. The MSB of the image is important because it contains most of the brightness information. There are three
bit planes R, G and B i.e. red, green and blue respectively for a colored image. The LSBof each bit plane is replaced by the
data after encryption which is to be safely transferred. For in- stance military data, confidential files etc. We replace LSB by the data because it is of least importance in formingthe image
to human eye. Stegnography is used for data hiding. But it is easy to extract back the data or the confidential information from the LSB and the data can be easily decoded. So to further secure the information we use the same key to decrypt the data. Due to the decryption process the sensitive information gets decrypted but the image remains as it was before. This decrypted image is transferred to the receiver. At the receiver end the same key is used to get back the shuffled image via encryption. Now the LSB is extracted and the data that was hidden can now be accessed.
IJSER © 2013 http://www.ijser.org
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-2013 1155
ISSN 2229-5518

4 INPUT IMAGE
5 ENCRYPTED IMAGE
6 DECRYPTED IMAGE

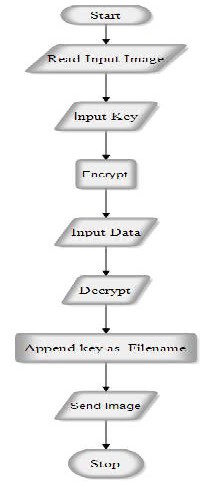
7 FLOWCHART: TRANSMITTER

IJSER © 2013 http://www.ijser.org
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-2013 1156
ISSN 2229-5518
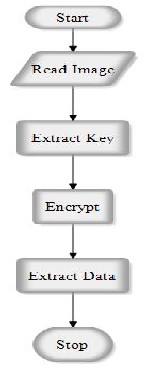
8 FLOWCHART: RECEIVER
9 CONCLUSION
The system aims at safeguarding the confidential in- formation being transmitted to the receiver. It is thus useful to convey important messages and strategies during wartime or when a there is some national emer- gency. As this technique consists of basic programming skills it can be adopted and used widely. But this tech- nique has its misuses. One of the most compelling arguments for controlling the use of digital stegno- graphic tools is the threat of terrorism. In early 2001, there were press reports that Osama bin Laden and others were using both encryption and stegnography
to hide maps , photographs of targets and instructions in pictures and text on various websites and various chat rooms.[3] It should thus be taken care that this- technology is not used for destructive purpose.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We would like to take this opportunity to thank the respected Principal Dr. Hari Vasudevan of D.J.Sanghvi College of Engi- neering and Head of Department of Electronics and Telecom- munication, Dr. Amit Deshmukh for guiding and supporting us. We would also like to thank Shri Vile Parle Kelavani Man- dal for their valuable encouragement for participating in such co curricular activities.
REFERENCES
[1] Debra Littlejohn Shinder, Ed Tittel, Scene of the Cybercrime: Com- puter Forensics Handbook, Syngress, 2002 - 512 pages Pg. 385
[2] Pro gram Analysis, Steganography, and Dynamic Transformation
Control, Pro-Quest, 2008 - 235 pages Pg. 16
[3] Michael J. Jochen, Internet Security: Hacking, Counterhacking, And
Society, Jones and Bartlett Learning, 2007 - 292 pages Pg. 209
IJSER © 2013 http://www.ijser.org





