International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 8, August-2013 1588
ISSN 2229-5518
Cost benefit analysis of adopting solar energy
pumps for jalswarajya schemes in Sangli district: A case study.
Mr. Rajiv Mohite, Dr. A. C. Attar, Mr. D. S. Patil
Abstract— The work undertaken to assess, Jalswarajya schemes in Sangli district resulted with reasons of scheme fail- ures, one of the reason for failure was high electrical charges for pumping water. This study was undertaken to provide an alternative solution to the same, one alternative we thought off was solar pumps instead of electrical. This paper highlights the benefits and cost analysis of using solar pumps, with case study details of application and calculations
are leistered in this paper.
1 INTRODUCTION
—————————— ——————————
Wind mills are stationary while solar systems can be
OUR world is full of energy. We can save money and help to
reduce air pollution using renewable energy sources such as solar
or wind power, for our home or irrigation (drip) or for live stock water wells. Wind and solar energy can be excellent options in remote areas where the cost of extending transmission lines are high or the cost of electricity charge is on higher side as well as there is cut off of electricity for more than 10 hours a day. It
is also important to consider the cost of buying and using a pumping system, which includes initial cost, energy cost and maintenance cost.
Where utility power is not readily available solar sys- tems are often the most economical option ,factoring in all costs, such as installation, fuel, maintenance and water pump- ing are often less expensive than generators, windmills and running electrical lines. With solar water pumping system a customer has an accurate forecast of the cost to run and main- tain them, as they have paid their energy cost up front. There may be tax credits and incentives that lower investment costs.
2. COMPARISON OF SOLAR SYSTEM WITH WINDMILL –
Both the initial and lifetime costs of solar powered system are far less than windmills due to lower shipping, in- stallation and maintenance costs.
Solar pumps operate anywhere the sun shines, while
windmills work where there is steady, constant wind supply.
————————————————
• Mr. Rajiv V. Mohite M.thec. (C&M) From Rajarambapu Institute of Technology Rajaramnagar,Islampur Distric – Sangli Maha- rashtra (India)E-mail:rajravi83@rediff.com.
• Dr. A. C. Attar professor in Civil Engineering Department, Rajaram- bapu Institute of Technology Rajaramnagar, Islampur Dis- tric – Sangli Maharashtra (India).
more easily moved to meet seasonal or variable location needs.
Depending on the application, a solar pumping sys- tem may use water storage tank which acts like a “water bat- tery” during cloudy weather but for wind mills there is no option.
Against this backdrop, renewable energy comes as the
perfect answer derived from natural processes. That is replen-
ished constantly and is sustainable in the sense that they can never run out. Moreover, solar energy the mother of all re- newable energies is the ideal solution. It is perfect combination of 3 Es
2.1 Energy – Solar energy is plentiful and virtually inex-
haustible. Studies shows that the energy needs of our entire planet can be addressed by the power of the Sun alone.
2.2 Ecology- Solar energy is clean, silent and generates no
waste. Thus it does not contribute to global warming or create
any environmental hazard. It allows compliance under the
Kyoto Protocol and where required, enables users to quality for carbon credits with reduced carbon footprints.
2.3 Economy: - Being free of cost solar energy always has an
attractive payback from the perspective of life cycle cost. At
best, it is fixed cost that is insulated against increasing energy
cost.
3. SOLAR PUMPING SYSTEM:-
3.1 Advantages:-
• Full day automatic operation Switch on and Off au- tomatically in the morning and evening respectively.
• Free and renewable source of energy.
• Saving in electricity Bills.
• Durable and reliable.
• Minimal maintenance required.
• Handy and easy to operate.
IJSER © 2013 http://www.ijser.org
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 8, August-2013 1589
ISSN 2229-5518
• Can replace conventional pumps where there is elec- tric grid.
• Pollution free and environmental friendly.
3.2 Features of solar inverter -
Battery less operation:-
Variable frequency drive incorporated for smooth op- eration even during minimum sun light. Transformer less design makes the product ‘cost effective’ and smaller in size.MPPT incorporated to track maximum power and gives 35% more energy from the panel. Maximum torque at minimum sunlight
3.3 Site requirements –
1. Space to mount panels.
2) Technically designed panel- Mounting structure.
3) Pump House to house inverter.
3.4 Product Performance Range:-
facts that power and fuel prices are inexorably climbing and power supply when available is also very erratic.
4. CASE STUDY :- DATA COLLECTION
Through the survey done in ten different villages from various tahasils, consumption of electricity for the Jalswarajya Scheme is one of the most important points for successful run- ning of Jalswarajya Scheme. Increase in unit rate of electricity increases the bill amount; this higher cost is one factor result- ing in scheme failure. Table 1.1 below shows these charges compared with income through water charges. Figure 1 shows the graphical representation of the same.
16
14
12
3.5 Prices of submersible/Surface solar water pump- 10
ing system for AC Pumps- 8
Battery less based solar water pumping system (Without pump) 6
Income Vs Electrical bill
i nc ome
el ectri ca l bi l l
4
2
0
Standard Pumping system consist of a) PV Array (Solar modules)
b) Pump.
c) Pump Controller
d) Safety disconnects and
e) Flushing.
The gap between supply and demand of electricity is
not only huge but widening by the day. Add to this, the grim
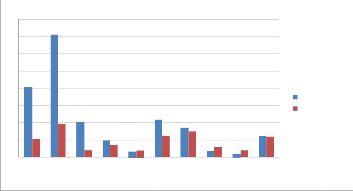
Looking at the income and electricity bills maximum share of income goes towards paying electricity bills, the share goes to
@ 60% for many villages. Higher electricity charges are due to higher distance between source to ESR (more than 5 Km) and the depth of well (Water) (15 M)
4.1 Using Solar Pump system to Village- Rethare Har-
naksh, Tahasil. Walwa.
The Jalswarajya Scheme – Successful.
3) Scheme Design : 40 Lpcd
IJSER © 2013 http://www.ijser.org
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 8, August-2013 1590
ISSN 2229-5518
6) As per 40 Lpcd water require : 3,25,320 Lit.
7) ESR Capacity : 1,50,000 Lit.
4.2 Pump Capacity Calculation:-
Village- Rethare Harnaksha (Walwa) Population - 8133
Per day demand – 40 Locd.
Water required /day = 8133 x 40 = 325320 Lit. = 325.32 M3
Assume- Average 5 Hrs. sun energy will be available
Water require per hour= 3, 25,320/5 = 65064 Lit/hr. Water required per minute 65064/60 = 1084 L/M
Say = 286.50 L/pm
Total lift for water
Well = 15 m.
raising main 5 m. Total Head = 30 M. ESR Height = 10 m
HP = Q x H /3.960
Where Q = Pump capacity
H = Total Lift. ( 3.785 Lit.= 1 G.)
Q= gallon = 1084/3.785 = 286.50 Gallon PM H = Feet = 30 x 3.281 = 98.43 feet
H = 286.50 x 98.43 / 3960
H = 7.12 Say 7.5 H.P. Converting HP to Watt Watt = HP x 746 Watt
= 7.5 x 746 = 5595 Watt.
Next to adjust the wattage to take in to consideration the loss of electricity in the cable and controls during transmission and in converting electricity to the mechanical movements of the pump. the average efficiency rate of these pumps is about
85%. To adjust for this inefficiency we must recalculate our power input.
Wattage needed = 3730/0.65 = 5595/0.85
6582.35 = Say 7 Kw
As per the company the Battery less based solar water pump- ing system (without pump costs).
5 KW water pumping system with PV panel mppt charger
inverters
for 5 HP pumps - 5,00,000.00
Pump Unit - 18,000.00
-------------------
Total Cost Rs. 5,18,000.00
Average life of the PV system = 20 years.
4.3 Panel and Pump design:-
Water required/day as 40 Lpcd
7.5 HP pump discharge = 1000 Lpm for 30 m Head. Total discharge in 5 hours
1000 x 60 = 60,000 Lit.
In 5 Hrs.= 60,000 x 5 = 3,00,000 Lit. Pump Specification:-
Pump HP = 7.5 HP Discharge = 1000 Lpm Head = 30 m
Rate of pump = 30,000/-
Panel Design –
1m x 2m Panel = 0.25 KW.
1 m x 2 m panel x 4 no. – 1 KW For 7 KW
Panel required = 4 x 7 = 28 ( 1x 2)
Area required for Panel fitting
1 x 2 x 28 = 56 m2
Add 100% more space for gap between the panel and area around it
Say = 56 m2 x 2 = 112 m2 = 1200 Sqft.

Arrangement of solar panels for solar system.
4.4 Stay required for Panel :-
Angle frame = 50 x 50 x 6 mm
7m x 2 +2 m x 2 = 18 m + 2 support (2 x 2 m) = 22 m. Stay required -
U/S 1.65 + 0.60 in ground = 2.25 m
C/C distance = 7’-00” Stay required 4 No. L/S 0.75 m + 0.60 in ground = 1.35 m
IJSER © 2013 http://www.ijser.org
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 8, August-2013 1591
ISSN 2229-5518
Stays required = 4 No. Total length of stays
2.25 x 4 + 1.35 x 4 = 14.40 m
For stays = 2” pipe For One stand. Angle 50 x 50 x 6 = 18 m + (2X2) = 22 m Pipe 50 x 6 = 14.4 m
Rate = Angle 42.50 = 124 Kg pipe- 12 Kg. 52 Kg. Excavation & Concrete = 8 pits = 0.6 x 0.3x 0.3
8 x 100/Pits = 800 Rs.
Concrete 0.054 m3 x 8 = 0.432 m3 (1:4:8)
0.432 x 4000/m3 = 1728 Rs.
Angle= 42.50 /Kg x 88 Kg = 3740-00
Pipe = 520/Kg x 30 Kg = 1560-00
Labor, Fabrication and coloring = 1000.No. Total for 1 Frame = 8828 Say Rs. 9000/-
A) For Four stands 9000 x 4 Rs.= 36,000-00
B) Rate for 7.5 Kw Panel = 5, 00,000-00
C) Inverter / Converter = 2, 00,000-00
D) Wiring connection and other Expenses = 30,000-00
---------------- Total 7, 66,000-00
Pump and Accessories 35,000-00
Total expenditure for 7.5 HP Pump Rs. 8, 01,000-00 and Solar inverter
5. PAY BACK PERIOD:
As we consider the life of solar system is 20 years. The Electric bill saving for 15 years
15 years x 2, 50,000 = 37, 50,000-00
6. CONCLUSION
In our country day by day the availability of electrici- ty by conventional methods is decreasing so the cost of elec- tricity is going on increasing which increases the load of ex- penditure on the Jalswarajya schemes in the dry area of Sangli district, which is one of the most important reasons behind the failure of schemes. The solar pump system is most economical remedy for the scheme. Solar pumping decreases the electric charges and save an amount up to 80%.which can be used for further improvement of Jalswarajya schemes. Also the pumps and equipment’s having low maintenance cost and zero run- ning cost which will decrease the operation and maintenance cost of the scheme up to 50%.Further it is ecofriendly.
7. REFRENCES:-
[1] Juan Enciso and Michael Mecko Texas Co-operative Ex- tension 6/04, Using Renewable Energy to pump water
[2] H.J. Helikson, D.Z. Haman and C.D Baird, University of Florida, Fact Sheet EES-63, November 1991, Pumping water for Irrigation using solar Energy.
[3] ProtonicsSystems India Pvt. Ltd. Noida. Quotation for So- lar water pumping system, Solar Water Pump Guide Coener- gy Us.
[4] Marathi Book on Jalswarajya by Water Supply and Sanitary department Maharashtra state.
[5] Dhananjay Patil, Krishna Solar Shoppy, Islampur. [6] Kriloskar Brothers Ltd. Kirloskar Pumping System. [7] MONO Pump Ltd. Litere Referencce June 2011
[8] Rural water supply department Zillah ParishadSan- gli.Latest states of Jalswarajya projects in Sangli district
Amount | Year | Elect.bill | Interest Rate 12% | Amount |
8,00,000 | 1 | 3,00,000 - 50,000 2,50,000 | 12% | 8,96,000 6,46,000 |
6,46,000 | 2 | 25,000 | 12% | 7,23,520 4,73,520 |
4,73,520 | 3 | 2,50,000 | 12% | 5,30,343 2,80,343 |
2,80,343 | 4 | 25,000 | | 30,342 33,984 |
33,984 | 5 | 25,000 | | 21,617 |
Total Loan recovery = 10, 33,983-00
Against the loan of Rs. 8, 00,000-00
Total payback period is 5 years.
IJSER © 2013 http://www.ijser.org

